How To Identify Fraudulent Digital Lending Apps? Types of Lending Frauds and Their Impact



It’s no doubt that Digital Lending Apps have taken the financial world by storm. They have changed the very ecosystem of borrowing and stand out by offering unprecedented convenience and accessibility to users.
But to every wonderful phenomenon, there will be a flip side. And digital lending is no exception.
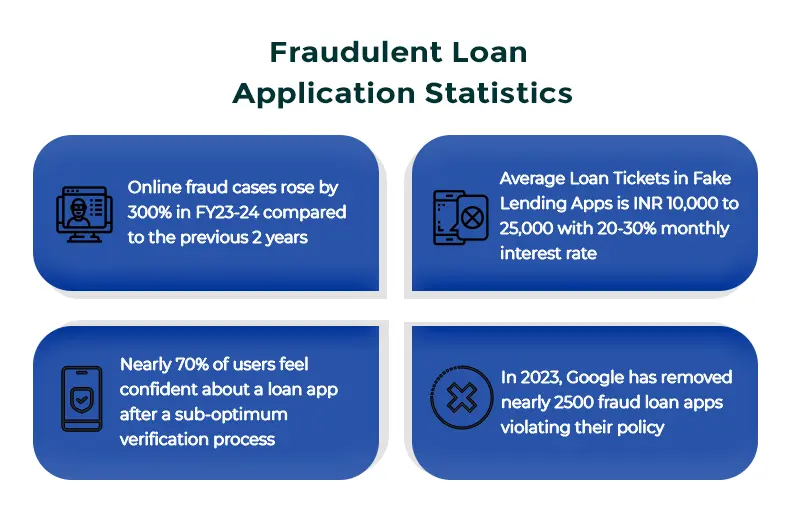
In FY 2023, banking fraud amounted to INR 300 million, of which 96% of the money is attributed to fraudsters receiving loans with the help of forged/ synthetic identities. And this is just one side of the coin. There are also multiple fraudulent loan apps in digital lending scamming common people, obtaining sensitive data with the promise of granting them loans and gaining access to their bank accounts, only to empty it and never be heard from again.
Now, imagine the amount of money being laundered daily by such fraudsters in different financial institutions and with the help of fake lending apps. Users and financial institutions need to be aware of the different types of digital lending scams to navigate this fraudster breeding ground until strong regulations are imposed and holistic cybersecurity solutions are adopted.
This article is aimed at educating and providing a comprehensive guide on online loan fraud in digital lending. Let’s dive in.
What are Fraudulent Lending Apps?
Fraudulent loan apps or Fake lending apps are digital platforms that are unauthorized and illegal loan providers impersonating authorized lending companies with loan management systems and loan origination systems. They primarily target low-income individuals and trick users into divulging their personal information or money.
Concerns Fake Loan Apps Raise
Typically, these loan app scams ask the users to pay an upfront fee by promising them hassle-free immediate loan grants without any credit or collateral checks. Some lending frauds charge exorbitant interest rates not approved by the government with the same promise. This results in users getting trapped in debt cycles and also more alarmingly facing harassment from fraudsters misusing their sensitive personal information.
On the other hand, due to these loan app scammers, financial institutions/ lenders face reputational damage and loss of trust with customers, in turn affecting their businesses. Since creating, distributing and popularizing these apps with the help of social media is very easy, coupled with inadequate regulations by the platforms and the lack of financial literacy among the general public, these fraudster apps have proliferated extensively, especially in the past decade.
Measures Taken to Combat Fraudulent Digital Lending Apps
There are several guidelines set by RBI in 2022 for digital lending apps to minimize such fraud cases and reduce illegal activities. Some of them are:
- Only Regulated Entities (REs), meaning banks, Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFCs), or their authorized Lending Service Providers (LSP) can operate Digital Lending Apps.
- Whether disbursement of approved loan amount or repayment of instalments/ loans, the deposits must be done directly to the RE or the borrower’s account. No third-party accounts shall be involved.
- No charges can be claimed by the Lending Service Provider to the borrower. All fees must be paid to the LSP directly by the RE.
- A Key Fact Statement (KFS) with the Annual Percentage Rate and all other inclusive costs must be furnished to the borrowers before executing contracts.
- The RE should publish a list of authorized LSPs and their digital lending apps on their website.
- Apps should ask for explicit consent from borrowers before collecting or sharing their data.
- All digital lending should be reported in the Credit Information Companies (CICs), regardless of tenure.
In addition to these guidelines, the latest update as of 2024 is that RBI is planning to set up a Digital Trust Agency (DIGITA) to address issues caused by illegal loan apps in India and its cyber frauds. Aimed at helping users differentiate between authorized loan origination systems and fraudulent loan apps, this proposed DIGITA would verify digital lending apps and maintain a public register of authenticated ones.
Additionally, since users are found to trust the legitimacy of apps if they are available in Google or Apple app stores, nearly 2,500 fraudulent loan apps have been removed by Google as of December 2023.
How To Identify Fake Lending Apps?
While regulations and measures are being taken from time to time, loan app scammers are also becoming increasingly tech-savvy and gullible people usually fall for their promises. To avoid getting inflicted with such lending frauds, we need to extend our awareness and knowledge on how best to spot these scammers and fraudulent loan applications.
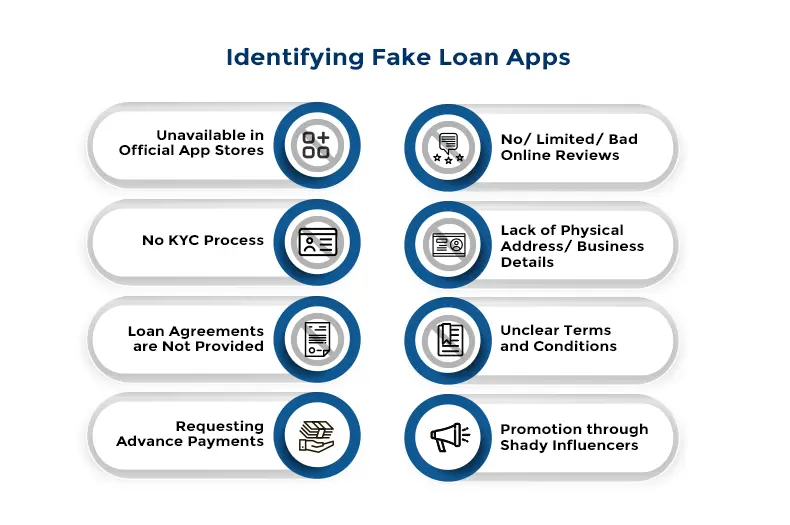
Here are some of the telltale signs of a fake lending app:
Unavailable in Official App Stores
Now that Google has taken measures to remove many fake apps from its store, many scammers are sending app files and asking users to download them. Authorized loan management systems do not do this and their digital platforms are available in official app stores.
No KYC Process
All loan applications require a Know Your Customer (KYC) process wherein the company collects information and government documents to verify the identity of the borrower. Reputable lenders always conduct this process and any application claiming that proper identity verification or credit score checks are not necessary is likely to be fraudulent.
Loan Agreements are Not Provided
As discussed earlier, RBI mandates lenders to provide a loan agreement with all key facts and details about the loan to the borrower. Fraudulent apps do not give a clear loan agreement document and it is a major warning sign.
Requesting Advance Payments
Fake lending apps typically demand upfront fees with the promise of returning them during loan disbursement before sanctioning the loan. Authorized digital lending platforms do not ask for any advance payments to process a loan.
No or Limited or Bad Online Reviews
It is wise to check online for the name of a lender and their reviews. If there are no or limited positive or complete negative reviews, they are likely fraudsters.
Lack of Physical Address/ Business Details
Authentic lending apps come up first when you do an online search with a proper physical business address along with website, contact no, working hours, long-time active social handles and reliable reviews. Fake lending apps typically do not have this clear physical and digital presence.
Unclear Terms and Conditions
Vague or confusing terms and conditions that are not explained properly by the lending app or their support team also indicate potential fraud.
Promotion through Shady Influencers
Unverified or suspicious social media profiles or influencers are signals of shadiness and point to fraudulent lending apps.
Other Red Flags
Additionally, unrealistic promises such as instant loan disbursement without background checks/ credit history checks, requests for unnecessary device data permissions, and intimidation or aggressive behaviour are all signs that you are dealing with a fake lending app.
Types of Frauds in Digital Lending Apps
We cannot talk about fraud in digital lending apps without discussing fraudulent behaviour both by lending apps and borrowers. Following is a list of frauds that come under both these umbrellas.
Personal Loan Fraud (first-party)
- In this case, fraudulent borrowers intentionally provide false information on loan applications.
- They may inflate income, fabricate employment details, or use fake documents.
- Loan stacking is common, where borrowers take multiple loans from different lenders simultaneously.
- These borrowers often have no intention of repaying, planning to default from the start.
Straw Buyer Fraud (second-party)
- Straw Buyer fraudulent borrowers recruit individuals with good credit to apply for loans on their behalf.
- They may offer a cut of the loan amount as compensation.
- The straw buyer might be aware of the fraud or could be manipulated into participating.
- Once the loan is approved, the fraudster takes the money, leaving the straw buyer liable.
Identity Theft (third-party)
- While often perpetrated by external criminals, some fraudulent borrowers engage in identity theft.
- They might steal personal information from friends, family, or colleagues to apply for loans.
- In account takeover scenarios, they gain unauthorized access to existing accounts to request loans.
Exorbitant Interest Rates
- This is primarily a lender-side issue, where apps charge extremely high interest rates.
- These rates are often hidden in complex terms and conditions to trap borrowers.
Mental harassment
- This fraud is typically perpetrated by lenders or their recovery agents.
- It involves aggressive collection practices, including threats and public shaming.
- Such practices cause severe mental distress to borrowers, often over minor defaults.
Premature Crediting
- This is a tactic used by fraudulent lenders to trap borrowers.
- They insist on crediting loan amounts before completing all formalities.
- This is then used as leverage for excessive charges or harassment.
Phishing
- Scammers send fraudulent emails or messages, posing as authorized lenders with in-house built loan management systems.
- The goal is to trick users into revealing personal and financial information.
Malicious software
- Some lending apps contain malware designed to gain unauthorized access to users’ devices.
- This can lead to stealing sensitive data or manipulating transactions.
Employee-Initiated Fraud
- This involves insider threats within lending organizations.
- Employees might create ghost borrowers or manipulate loan approvals for personal gain.
Fake Physical Addresses
- Fraudulent apps may list non-existent or incomplete physical addresses to appear trustworthy.
- This makes it difficult for authorities to track them down.
Impact of Fraudulent Apps
For Borrowers
Borrowers or the common people who fall prey to these fake lending apps are the ones impacted the most by these cyber crimes. Some of the alarming issues they face are:
Identity theft: Personal information stolen and misused for various fraudulent activities.
Financial loss: By paying upfront fees or account information enabling scammers to empty the borrower’s funds, borrowers often go into debt cycles.
Credit damage: As a result of identity theft, this happens when unauthorized loans are taken out of the borrower’s name leading to a credit score fall.
Emotional distress/ Legal issues: With low-income individuals facing financial ruin and with others facing reputation loss owing to harassment or misuse of personal information, people can become emotionally distressed and might even have suicidal thoughts. Some individuals decide to take the help of the legal system, resulting in a struggle and expenditure of time and money proving they were victims of lending fraud.
For Lenders
Although the impact of such fraud is prominent on individual borrowers, authorized digital lending apps with loan management systems on the other hand, also face fatal consequences.
Reputational damage: When fraudulent loan apps misrepresent themselves as established lenders, they erode the trust of the customers and potential clients, leading to irreparable reputation damage.
Financial loss: Financial losses occur through fraudulent loan applications that slip through verification processes. Additionally, owing to reputation damage, lenders lose out on prospects and business leading to a substantial financial burden.
Regulatory Scrutiny: With the loss of trust or compromise on user data, comes regulatory scrutiny. It can potentially lead lenders to pay hefty fines and further erosion of trust. These issues and scrutiny can have long-lasting effects on a lender’s market position and growth prospects.
Our Takeaway
In digital solutions, the balance between user convenience and data security has always been intricate. Government measures and the current regulatory landscape have significant gaps in identifying and preventing such fraudulent loan apps in digital lending. Unfortunately, these app scammers are also evolving day by day, and they operate in a grey area exploiting gullible borrowers.
The lack of seriousness by social media platforms in framing regulations for these promotions is further worsening the situation. These online loan frauds are complex in nature and they demand collective efforts from all stakeholders: from regulators, and financial institutions to technology companies, and end users.
There is an urgent need to create a secure and ethical ecosystem with digital lending apps focusing on stringent technology and cybersecurity measures. CloudBankin’s state-of-the-art encryption features, VAPT testing and cyber security plug-ins are aimed to do just that.
Ultimately, combating fraudulent lending apps necessitates a multi-pronged approach involving legal, technological, and educational initiatives. Only through such concerted efforts can we ensure that digital lending fulfils its promise of financial inclusion without compromising user safety and trust.
Related Post

Gold Loans – the Whats, Hows and Whys
Shiny, pure and incredibly valuable, gold is the metal that’s

The Indian Loan Management System – During and After the Pandemic
The pandemic has affected individuals, businesses, communities and economies globally.
Why Should You Use A Cloud-Based Loan Management Software
In today’s competitive market, people are lacking behind in time
- Email: [email protected]
- Sales Enquiries: +91 9080996606
- HR Enquiries: +91 9080996576
Quick Links
Resources
© 2025 LightFi India Private Limited. All rights reserved.
(Formerly known as Habile Technologies)